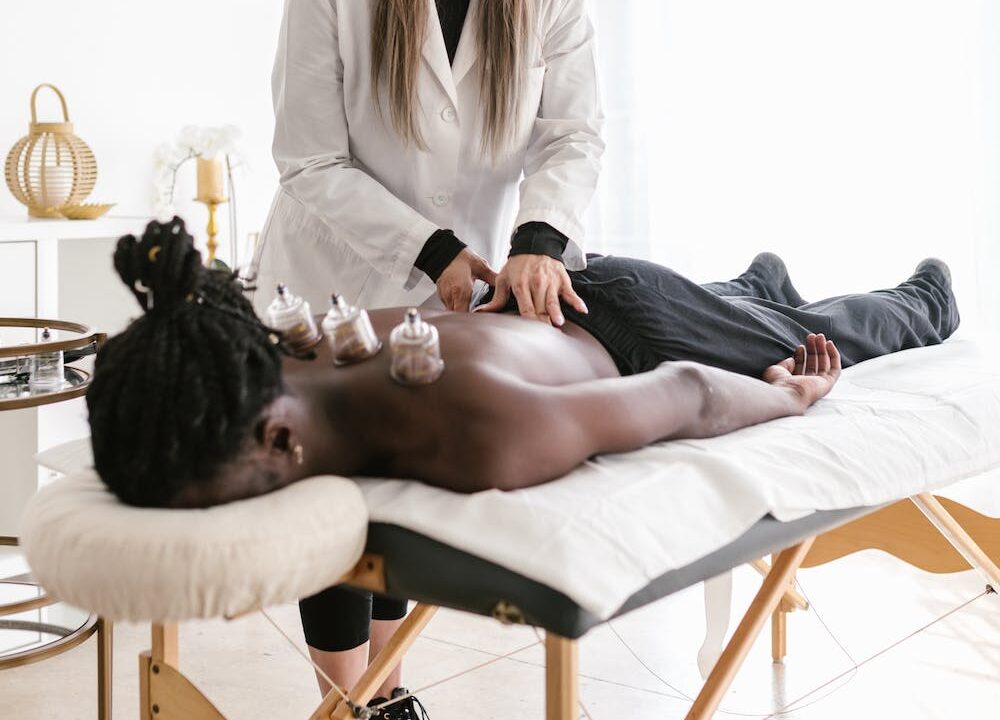
Cupping therapy is an ancient technique that has gained popularity in recent years. It involves placing cups on the skin to create suction and is used for pain relief and musculoskeletal injuries. The history of cupping therapy dates back thousands of years, with roots in ancient Egyptian, Chinese, and Middle Eastern cultures. It is considered one of the oldest treatment interventions, with its origins dating back to 1500 B.C.
The theory behind cupping therapy is based on the concept of stagnation and pain. The idea is that where there is stagnation, there is pain, and by removing the stagnation, the pain can be alleviated. Cupping therapy creates a negative pressure environment by placing cups made of glass, plastic, bamboo, or ceramic on the skin. The cups can be applied to various areas of the body where it’s easy to attach them, such as the back, shoulders, stomach, and legs.
There are two types of cupping methods: wet and dry. Dry cupping involves using a pumping method to draw the skin tissue into the cup. The cups can either slide across the skin or remain in place, known as dynamic and stagnant cupping, respectively. Wet cupping goes a step further by creating a mild suction and then using a small scalpel to make a tiny cut on the skin. A second suction is then used to draw out a small amount of blood.
Key Takeaways:
- Cupping therapy is an ancient technique that involves placing cups on the skin to create suction.
- The theory behind cupping therapy is based on the concept of stagnation and pain.
- There are two types of cupping methods: wet and dry.
The History of Cupping Therapy
The history of cupping therapy dates back thousands of years, with roots in ancient Egyptian, Chinese, and Middle Eastern cultures. It is considered one of the oldest healing interventions and has been used for various purposes, including pain relief, muscle tension, and detoxification. The earliest record of cupping therapy dates back to 1500 B.C. in Egypt, where it was used to treat pain, fever, and menstrual imbalances.
In Chinese medicine, cupping therapy is known as “ba guan,” which means “to pull out illness.” It was used for various conditions, including respiratory diseases, digestive disorders, and skin conditions. The Chinese also used cupping therapy as part of their martial arts practice to help relieve muscle tension and promote recovery.
The Middle Eastern culture also embraced cupping therapy, with references to it in the ancient Islamic texts. The Prophet Muhammad is said to have practiced cupping therapy and recommended it as a treatment for various ailments.
Despite its long history of use, cupping therapy remains controversial in modern medicine. Some clinicians believe it has no therapeutic value, while others see it as a valuable complementary therapy for certain conditions. The research on cupping therapy is limited, and more high-quality studies are needed to determine its efficacy.
The Theory Behind Cupping Therapy
The theory behind cupping therapy is based on the concept of stagnation and pain. When there is stagnation in the body, it disrupts the flow of energy, or Qi, which can lead to pain and discomfort. Cupping therapy aims to create negative pressure and suction, which helps to remove stagnation and promote the flow of Qi throughout the body.
According to traditional Chinese medicine, cupping therapy can help to stimulate the immune system, increase blood flow, and relieve muscle tension. By creating suction and negative pressure, cupping can also help to break up adhesions and scar tissue, which can improve range of motion and reduce pain.
There are different techniques used in cupping therapy, including static cupping, sliding cupping, and flash cupping. Static cupping involves leaving the cups in place for several minutes, while sliding cupping involves moving the cups over a larger area. Flash cupping involves quickly applying and removing the cups, which can help to stimulate the nervous system.
While there is limited scientific research on the benefits of cupping therapy, many people who have undergone the treatment report feeling more relaxed and experiencing a reduction in pain and muscle tension. Some studies have suggested that cupping therapy may be effective for treating certain conditions such as back pain, migraines, and osteoarthritis. However, more research is needed to confirm these findings.
“Cupping therapy aims to create negative pressure and suction, which helps to remove stagnation and promote the flow of Qi throughout the body.”
The Cupping Therapy Process
Cupping therapy creates a negative pressure environment by placing cups made of glass, plastic, bamboo, or ceramic on the skin. The cups are warmed or filled with hot air and then placed on the skin, creating a vacuum that draws the skin and underlying tissue into the cup. The cups can be applied to various areas of the body, including the back, shoulders, stomach, and legs.
There are different methods of cupping therapy, including:
| Dry Cupping | Wet Cupping |
|---|---|
| Dry cupping involves using a pumping method to draw the skin tissue into the cup. The cups can either slide across the skin or remain in place, known as dynamic and stagnant cupping, respectively. | Wet cupping goes a step further by creating a mild suction and then using a small scalpel to make a tiny cut on the skin. A second suction is then used to draw out a small amount of blood. |
The length of time the cups are left in place depends on the individual needs of the patient and the practitioner’s assessment of their condition. The cups are typically left in place for 5-15 minutes. The practitioner may also apply massage techniques before or after the cups are applied to further stimulate blood flow and relaxation.
While cupping therapy is generally safe when performed by a licensed practitioner, it may cause temporary bruising, swelling, or soreness. The bruises left behind typically fade after several days or a week. Some people may experience side effects such as feeling lightheaded, dizzy, or flu-like symptoms such as nausea and body aches.
In summary, cupping therapy involves creating a vacuum on the skin using cups made of glass, plastic, bamboo, or ceramic. The cups may be left in place for several minutes and can be applied using dry or wet cupping methods. While there are risks associated with cupping therapy, it can be safe and effective when performed by a licensed practitioner. It’s important to consult with a healthcare provider before considering cupping therapy or any alternative or complementary medicine.
Dry Cupping vs Wet Cupping
There are two types of cupping methods: wet and dry. Dry cupping involves using a pumping method to draw the skin tissue into the cup. The cups can either slide across the skin or remain in place, known as dynamic and stagnant cupping, respectively.
Wet cupping goes a step further by creating a mild suction and then using a small scalpel to make a tiny cut on the skin. A second suction is then used to draw out a small amount of blood. This method is believed to remove harmful substances from the body and is sometimes used for detoxification purposes.
Both methods can be used to address pain and musculoskeletal conditions, but wet cupping should only be performed by licensed professionals due to the potential for infection and other risks.
It’s important to note that cupping therapy may not be suitable for everyone, and individuals with certain conditions may be more at risk for complications. Always consult with a licensed healthcare provider before considering cupping therapy or any alternative or complementary medicine.
The Safety of Cupping Therapy
Cupping therapy is generally safe when performed by a licensed practitioner. It may cause temporary bruising, swelling, or soreness, but it shouldn’t be painful. The bruises left behind typically fade after several days or a week. Some people may experience side effects such as feeling lightheaded, dizzy, or flu-like symptoms such as nausea and body aches.
However, it’s important to note that cupping therapy is not suitable for everyone. There are certain risks and contraindications to consider before undergoing the treatment. Cupping can leave behind hickey-like bruises on the skin and may worsen conditions such as eczema or psoriasis. There is also a small risk of skin infection, especially if wet cupping is involved. It is not recommended for individuals with certain health conditions such as liver, kidney or heart failure, pacemakers, hemophilia, anemia, blood disorders, heart disease, or those on blood thinners. Pregnant women are advised to avoid cupping on the abdomen and lower back.
Cupping Therapy Side Effects
While cupping therapy is generally safe, there are potential side effects to be aware of. These include:
- Bruising and skin irritation
- Feeling lightheaded or dizzy
- Nausea or flu-like symptoms
- Worsening of skin conditions such as eczema or psoriasis
- In rare cases, skin infections or scarring
Cupping Therapy Research
There has been limited scientific research on cupping therapy. While some studies suggest that it may help with pain relief, acne, herpes zoster, and certain musculoskeletal conditions when combined with other treatments such as acupuncture or medications, many of these studies are considered low quality and biased, indicating a need for further research.
It’s important to consult with a healthcare provider before considering cupping therapy or any alternative or complementary medicine. They can assess if cupping therapy is suitable for your specific condition and advise on the best course of treatment. Cupping therapy can be complementary to existing treatment plans, but it should always be performed by trained and licensed professionals to ensure safety and effectiveness.

The Benefits of Cupping Therapy
The benefits of cupping therapy are often touted, but there is limited scientific evidence to support these claims. However, many people report reduced pain, muscle tightness, and inflammation after a cupping session. Cupping therapy has also been used for detoxification purposes, with some individuals claiming to feel rejuvenated and relaxed after a session. Additionally, improved blood flow and increased range of motion are some of the other reported benefits.
Cupping therapy is an effective treatment for pain relief and musculoskeletal injuries. It is often used as an adjunct therapy with acupuncture or massage to help alleviate pain and discomfort. Cupping therapy can be especially effective in treating back pain, shoulder pain, and knee pain. It can also be used to help with digestive issues, headaches, respiratory problems, and menstrual disorders.
Cupping therapy has been shown to have a positive impact on the body’s immune system. It can help to boost immunity and enhance overall health. The therapy has been used to treat a wide range of illnesses, including colds, flu, and allergies.
While the benefits of cupping therapy are not completely understood, it remains a popular alternative therapy for many individuals seeking relief from pain and discomfort. As with any alternative therapy, it’s important to consult a healthcare provider before trying cupping therapy to ensure it’s safe and appropriate for your specific needs.
The Risks of Cupping Therapy
There are few risks associated with cupping therapy, but it’s important to be aware of potential side effects. As mentioned previously, cupping therapy can cause temporary bruising, swelling or soreness, which should fade after several days or a week. However, some people may experience other side effects such as feeling lightheaded, dizzy or flu-like symptoms such as nausea and body aches.
While cupping therapy is generally safe, it may worsen certain conditions such as eczema or psoriasis. There is also a small risk of skin infection, especially if wet cupping is involved. It is not recommended for individuals with certain health conditions such as liver, kidney or heart failure, pacemakers, hemophilia, anemia, blood disorders, heart disease, or those on blood thinners. Pregnant women are advised to avoid cupping on the abdomen and lower back.
It’s important to understand that while cupping therapy has gained popularity, there is limited scientific evidence to support its effectiveness as a treatment. It’s always wise to consult with a healthcare provider before considering cupping therapy or any alternative or complementary medicine. They can assess if cupping therapy is suitable for your specific condition and advise on the best course of treatment. Cupping therapy can be complementary to existing treatment plans, but it should always be performed by trained and licensed professionals to ensure safety and effectiveness.
Scientific Research on Cupping Therapy
In terms of scientific research, there have been limited studies on cupping therapy. However, some studies have been conducted to investigate the potential benefits and risks of cupping therapy.
One systematic review of 135 studies found that cupping therapy may provide short-term relief for conditions such as neck pain, low back pain, and carpal tunnel syndrome. The review also found that cupping therapy may have a mild to moderate effect on reducing pain intensity compared to no intervention or conventional treatments, but the quality of the studies was generally low.
| Condition | Research Findings |
|---|---|
| Pain relief | Some studies suggest that cupping therapy may help reduce pain intensity and improve function in conditions such as neck pain, low back pain, and carpal tunnel syndrome, but further research is needed to confirm these findings. |
| Skin conditions | Some studies suggest that cupping therapy combined with other treatments may help improve skin conditions such as acne and herpes zoster. |
| Musculoskeletal conditions | Some studies suggest that cupping therapy may improve pain and stiffness in conditions such as osteoarthritis and fibromyalgia when combined with other treatments, but more research is needed to confirm these findings. |
Another study found that cupping therapy may improve blood flow and reduce muscle soreness in athletes. However, this study was small and further research is needed to confirm these findings.
Despite the limited scientific research, cupping therapy remains popular among athletes and those seeking alternative or complementary treatments for pain relief and musculoskeletal injuries. It’s important to keep in mind that the evidence for the effectiveness of cupping therapy is still preliminary, and more high-quality research is needed to confirm its benefits and risks.
Individuals should always consult with a healthcare provider before considering cupping therapy or any other alternative or complementary medicine. A licensed practitioner should perform the cupping therapy to ensure safety and effectiveness.

Conclusion
It’s important to consult with a healthcare provider before considering cupping therapy or any alternative or complementary medicine. While cupping therapy has gained popularity in recent years and has been used for thousands of years, there is limited scientific evidence to support its reported benefits. However, it can be complementary to existing treatment plans for pain relief, muscle tightness, and inflammation when performed by trained and licensed professionals.
As with any medical treatment, there are potential risks and side effects to be aware of, such as temporary bruising, swelling, or soreness. It’s important to understand these risks and contraindications, especially if you have certain health conditions or are pregnant.
More research is needed to fully understand the effectiveness and safety of cupping therapy. In the meantime, it’s essential to discuss all treatment options with your healthcare provider and work together to determine the best course of action for your specific needs.
FAQ
Q: How does cupping therapy work?
A: Cupping therapy involves placing cups on the skin to create suction. This suction creates a negative pressure environment, which is believed to help alleviate pain and promote healing.
Q: What is the history of cupping therapy?
A: Cupping therapy dates back thousands of years and has roots in ancient Egyptian, Chinese, and Middle Eastern cultures. It is considered one of the oldest treatment interventions, with origins dating back to 1500 B.C.
Q: What is the theory behind cupping therapy?
A: The theory behind cupping therapy is based on the concept of stagnation and pain. By creating suction, cupping therapy aims to remove stagnation and relieve pain.
Q: What are the different cupping methods?
A: There are two types of cupping methods: dry and wet. Dry cupping involves creating suction without bloodletting, while wet cupping involves making a small cut on the skin and then creating suction to draw out a small amount of blood.
Q: Is cupping therapy safe?
A: Cupping therapy is generally safe when performed by a licensed practitioner. However, there may be temporary side effects such as bruising, swelling, or soreness. It is important to consult with a healthcare provider before undergoing cupping therapy.
Q: What are the reported benefits of cupping therapy?
A: Some reported benefits of cupping therapy include reduced pain, muscle tightness, inflammation, improved blood flow, and increased range of motion. However, more research is needed to confirm these claims.
Q: What are the potential risks of cupping therapy?
A: Cupping therapy may leave bruises on the skin and can worsen conditions such as eczema or psoriasis. There is also a small risk of skin infection, especially with wet cupping. It is not recommended for individuals with certain health conditions or those on blood thinners.
Q: What does scientific research say about cupping therapy?
A: There is limited scientific research on cupping therapy, and many studies are considered low quality and biased. While some studies suggest potential benefits, more high-quality research is needed to confirm these claims.
Q: How should I approach cupping therapy?
A: It is important to consult with a healthcare provider before considering cupping therapy. They can assess if it is suitable for your specific condition and recommend the best course of treatment. Cupping therapy should only be performed by trained and licensed professionals to ensure safety and effectiveness.